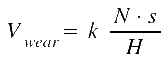
Where:
Home Search Reference Manuals Return
The model of the track in substructure file wr_coupl_pra1.ins is built up in a very similar way as the substructure file wr_coupl_pr1.ins. The main difference between wr_coupl_pr1.ins and wr_coupl_pra1.ins is that instead of using a lookup table as in file wr_coupl_pr1.ins, file wr_coupl_pra1.ins calculates the creep forces according to Kalker's simplified theory.
In substructure file wr_coupl_pra1.ins the wear of wheels and rails are
calculated according to Archard's wear model:
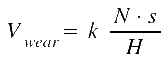
Where:
| Vwear | = | Volume of wear [m3] |
| k | = | Wear coefficient [1] |
| N | = | Normal force [N] |
| s | = | The sliding distance [m] |
| H | = | The hardness of the softer material [N/m2] |
The wear coefficient k is not constant for all sliding speeds and contact pressures, because different regions have different kind of wear mechanisms. The wear coefficient k is defined in a wear chart.
Example:

In addition to the required input data variable names in wr_coupl_pr1.ins above, substructure file wr_coupl_pra1.ins also requires the following variables:
| H | = | Hardness in Vickers N/m2 |
| Arch_speed_borders | = | Speeds, separating the different regions in the wear chart |
| Arch_press_borders | = | Pressures separating different regions of the wear chart |
| Arch_wear_coeff | = | Wear coefficients for the different wear regions in the wear chart |
The code of the substructure can be read in the file $gensys/calc/insert_files/wr_coupl_pra1.ins
The input and output parameters are defined under command func wr_coupl_pra1