If you are missing VirtualBox or if your VirtualBox-version is older than 6.1.40, it is necessary to do these steps:
-
Make sure your machine is equipped with a 64-bits processor.
Primary memory > 1 GB
Free hard disk space > 55 GB
Restart your machine and check in your BIOS that Virtualization Technology is enabled.
Information on how to adjust BIOS-settings can be found here: wikihow or lifewire - If necessary, uninstall the old VirtualBox-version.
-
Microsoft C and C++ runtime libraries must be installed before VirtualBox 7 can be installed:
Please go to: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-US/cpp/windows/latest-supported-vc-redist?view=msvc-170
and download one of the packages ARM64, X86 or X64, depending on the architecture of your computer. On a Windows host you can see the architecture, use these steps:- Open Start.
- Search for "msinfo32" and click the top result to open the System Information app.
- Under "System Type" you can see the architecture of your computer.
-
Also "Python" must be installed before VirtualBox 7 can be installed:
Please go to: https://www.python.org/downloads/
Once python is downloaded and installed:- Open Start.
- Search for "cmd".
- Run program "cmd" as administrator
- Go to the location where Python was installed. (The default installation directory for Python is %HOMEPATH%\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python###)
-
Execute the following command:
python -m pip install pywin32
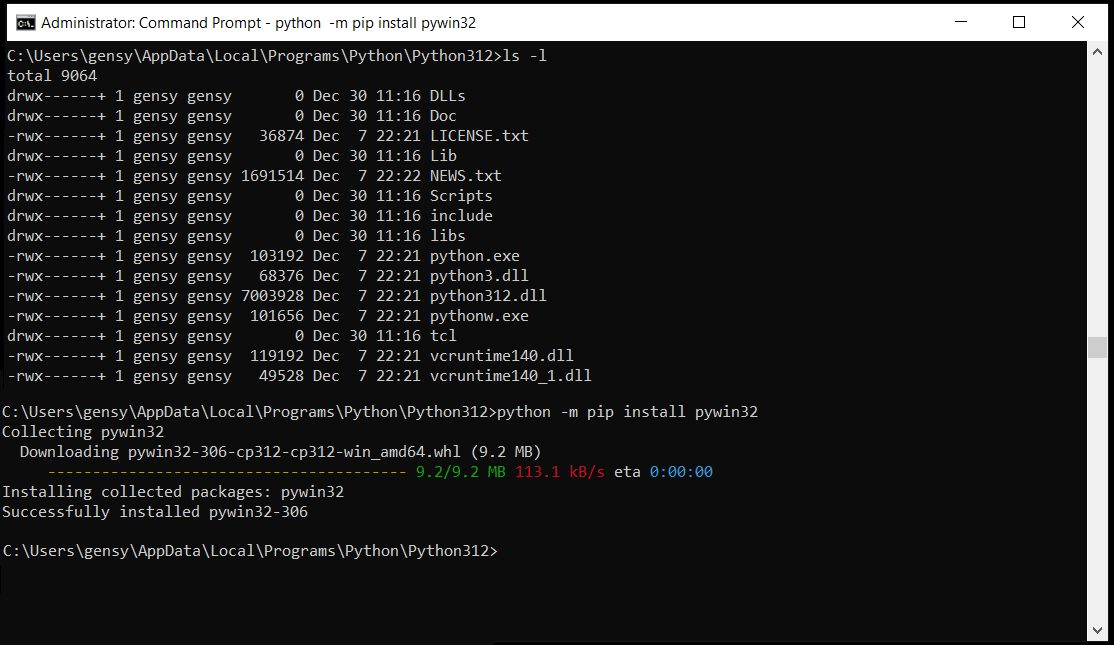
Now VirtualBox 7 is ready to be installed. - Download and install VirtualBox 7.0.12 or newer.
-
Start program VirtualBox
-
In the PullDown-menu of program VirtualBox click "File -> Preferences"
On the left side in the popup-window select "Input"
On the right side select "Virtual Machine"
As default in VirtualBox "Host Key Combination" is set equal to Right CTRL. If you wish to be able to use your "Right CTRL"-Key, please choose another key. (The "Host Key Combination" is mainly useful in case you don't have a working mouse, and when you want to leave full screen mode)
Finish by clicking "OK"
N.B. In this step you will create the following three directories: free_models, homepage and verif. If you have old versions of these directories, they will be overritten.
If you want to keep your old versions of free_models, homepage and verif. You can skip this part, or you can uncompress the files at another location, and then compare the directories with each other using script opdiff_dir.
-
Create a directory where you want to keep Gensys documentation files, verification examples
and your own workfiles.
The directory must have permissions so it can be used as a Shared Folder with the virtual machine.
E.g.: "C:\Users\Public\gensys" on a Windows-host or "$HOME/gensys" on a UNIX-host. -
In the newly created work directory.
Also create a directory where you can keep your own work files.
E.g.: "analyse" -
Download the following files:
free_models-2301.7z = Free vehicle models homepage-2301.7z = Documentation and tutorials verif-2301.7z = Verification directory
Webpage mega.nz requires a webbrowser that handles HTML5 and allows JavaScript to create and write to files. Currently Chrome and Firefox works best.
Also make sure that no firewall prevents you from downloading files from the Internet.
The SHA256 message digest algorithm should give you the following output:ec00a0676f1475ad6d416b67e13e771a51494886678ccfe3706df6b4ca58915a free_models-2301.7z e464fe7ffa0ff80de930ea86ddcad3904ac68404be1ad8491594a90d92a2c6ec homepage-2301.7z fd87572e0d809aaa1b3806f624320dfafe36422fabefb95554f23c35a90a25ab verif-2301.7z
The above output can be created with the following commands:
UNIX: sha256sum [a-z]*7z
Windows: certutil.exe -hashfile free_models-2301.7z SHA256 certutil.exe -hashfile homepage-2301.7z SHA256 certutil.exe -hashfile verif-2301.7z SHA256
-
Move the downloaded files to your Shared Folder (E.g. C:\Users\Public\gensys" or "$HOME/gensys").
Uncompress the files in program that handle 7-zip files.
(If you don't have a program for 7-zip files,
you can download a program with this link: www.7-zip.org/download.html)
When unzipping the 7-zipped files, please uncheck the checkbox under "Extract to:", otherwise the zipped files will not be extracted to the correct location. E.g.: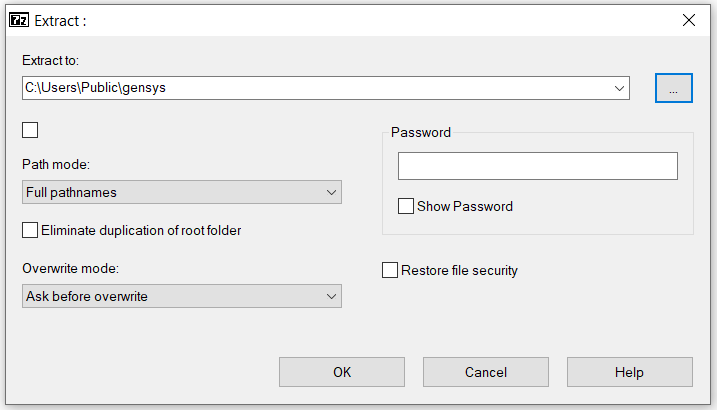
After 7-zipped files have been unzipped your directory should look as follows: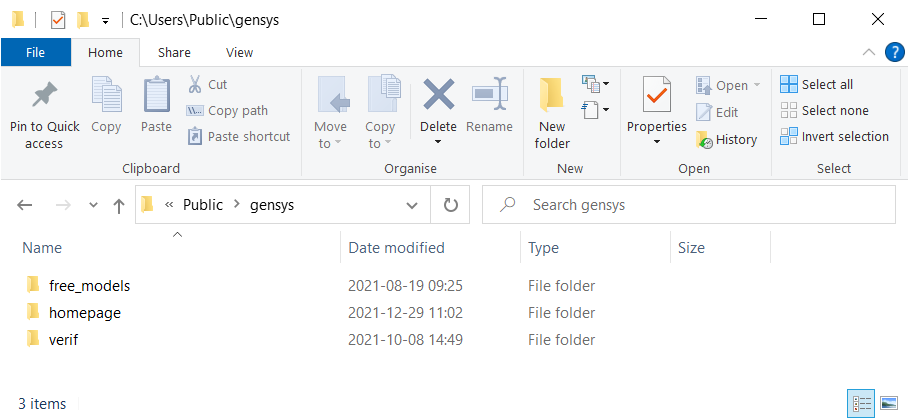
- The files free_models-2301.7z, homepage-2301.7z and verif-2301.7z can now be removed.
-
Download the following 7-zip files:
Mint21-gensys23.7z.001 Mint21-gensys23.7z.002 Mint21-gensys23.7z.003 Mint21-gensys23.7z.004 Mint21-gensys23.7z.005 Mint21-gensys23.7z.006 Mint21-gensys23.7z.007 Mint21-gensys23.7z.008
N.B webpage mega.nz requires a webbrowser that handles HTML5 and allows JavaScript to write files. Currently Chrome and Firefox works best.
Also make sure that no firewall prevents you from downloading files from the Internet.
The SHA256 message digest algorithm should give you the following output:2cbd64707925d92264725f64b33510a55b666b9f4d80631a8cf87e19d50cb848 Mint21-gensys23.7z.001 11c47204aff0644a923501bc9abd1dccf406058fdcfb5cb746837e19bd9828a9 Mint21-gensys23.7z.002 7a0d86abc3bee28800a9a44ea29265d234d1dab4ab1eab149556bbbaff97be35 Mint21-gensys23.7z.003 c4bade60e808dab16a9ebbe7e7e2ecc2c46916d00491e36110fa001d1254ba53 Mint21-gensys23.7z.004 caccf47ea79f2761c76935d0839c08d51ff6bd5695d616ac40e5a4c3d2371ff9 Mint21-gensys23.7z.005 bb6d9ebbbe6ff5eaa5b5c862db02181436be4e09bcb1c5a61517796f28f6b0a1 Mint21-gensys23.7z.006 17f6fe09a8c6dab4fbed7da941a1dbcf1b317504350b9425d46206efc810eb57 Mint21-gensys23.7z.007 842ab27f2e10d11b2c551d2aaccba437aa96caa29d2b62841caf7ea929a4f3ac Mint21-gensys23.7z.008
The above table can be obtained with the following command(s):UNIX: sha256sum Mint21-gensys23.7z.00?
Windows: certutil.exe -hashfile Mint21-gensys23.7z.001 SHA256 certutil.exe -hashfile Mint21-gensys23.7z.002 SHA256 certutil.exe -hashfile Mint21-gensys23.7z.003 SHA256 certutil.exe -hashfile Mint21-gensys23.7z.004 SHA256 certutil.exe -hashfile Mint21-gensys23.7z.005 SHA256
- Contact info@gensys.se to get a link to a valid license file for your installation.
-
Create a directory for your virtual machines.
If you are installing a virtual machine for the very first time. Please create a directory to store your virtual machines in. E.g.: "C:\Users\Public\VirtualBox VMs" on a Windows-host or "$HOME/VirtualBox VMs" on a UNIX-host.
-
Uncompress the file archive.
Move the files downloaded under 3.1) to the location created under 3.3).
Mark file "Mint21-gensys23.7z.001" and with your right mouse button and select 7z -> Open Archive -> Extract.
After the virtual machine has been extracted, the files "Mint21-gensys23.7z.00[1-8]" can be removed.
(If you don't have a program for 7-zip files, you can download a program with this link: www.7-zip.org/download.html)
When unzipping the 7-zipped files, please uncheck the checkbox under "Extract to:", otherwise the zipped files will not be extracted to the correct location. E.g.: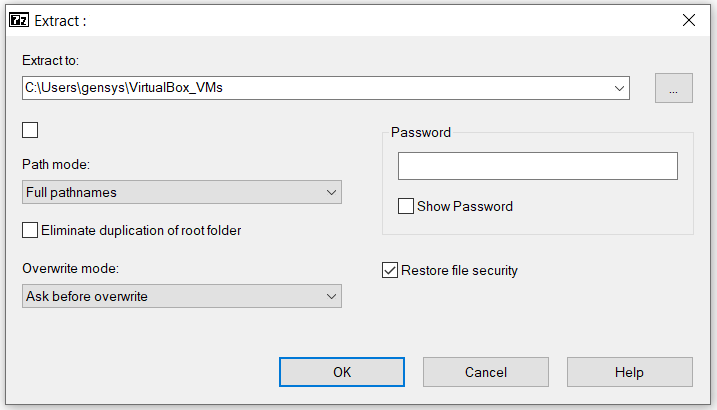
After 7-zipped files have been unzipped your directory should look as follows: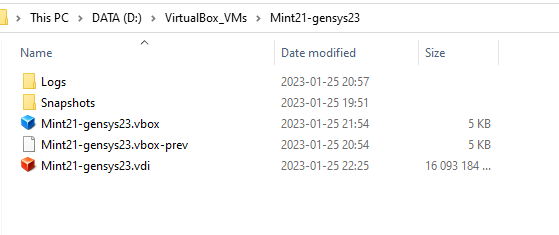
-
Setup the virtual machine.
Go to the newly created directory "Mint21-gensys23". Start VirtualBox by double-clicking file "Mint21-gensys23.vbox".
Mark the virtual machine "Mint21-gensys23" and click "Settings".-
Activate Shared Clipboard
On the left side in the popup-window select "General"
On the right side select "Advanced"
Under "Shared Clipboard" choose Bidirectional
Under "Drag'n'Drop" choose Bidirectional -
Set primary memory
On the left side in the popup-window select "System"
On the right side select "Motherboard"
Choose how much primary memory the virtual machine will have access to with the scale "Base Memory". Minimum recommended size is 1280MB. Maximum recommended size depend on the size of the primary memory of your host computer. You must choose a size within the green marked area of the scale. -
Set number of processors
On the left side in the popup-window, select "System"
On the right side, select "Processor"
Set number of processor(s) of your machine.
Valid number of processors are marked in green. -
Activate Shared Folders
On the left side in the popup-window select "Shared Folders"
On the right side select "gensys D:\gensys"
Click right mouse button and select "Edit Shared Folder"
Change "Folder Path" so it points to your "Shared Folder"-location. See under "Download and uncompress the documentation and the verification examples" above.
Folder Name: "gensys" must not be changed (N.B. Folder Name is case sensitive)
Do not check "Read-only".
Do not check "Auto-mount".
Leave text field "Mount point" blank
Check "Make Permanent" (if the option is visible)
Click OK
-
Activate Shared Clipboard
- In the VirtualBox main window, start the virtual machine by clicking the green arrow marked "Start"
-
Install Gensys license file.
Start webbrowser firefox in the virtual machine. Enter the link mentioned under 3.2) above, and download the file. Save the license file in directory "/opt/gensys/gensys-2301/bin".
Add execute permissions to file gen_processor_ID_check:
chmod +x /opt/gensys/gensys-2301/bin/gen_processor_ID_check
-
Configure the slurm queue system by editing file: /etc/slurm/slurm.conf
Under "NodeName", set number of available processors for each node in the cluster.
If you have many machines in your cluster, command "NodeName" can be given multiple times.
After the file /etc/slurm/slurm.conf has been updated, the virtual machine must be restarted in order to make the changes to take effect. restart the slurm queue system by writing:
sudo /etc/init.d/slurmd stop sudo /etc/init.d/slurmd start sudo /etc/init.d/slurmctld stop sudo slurmctld
In a terminal window: Test slurm by running program "/bin/hostname" via command sbatch:sbatch --output=sbatch.out <<+ #!/bin/sh /bin/hostname +
Output from the command will be sent to file sbatch.out
If file sbatch.out don't appear in your current work directory. Check if you can see the job in the Slurm graphical user interface:
sview &
If the status of the job is "PENDING". Open program "Oracle VM VirtualBox Manager" and go to Settings -> System -> Processor, and check that number of processors are greater or equal to the number defined in file /etc/slurm/slurm.conf.
If not, update file /etc/slurm/slurm.conf again, or shutdown the virtual machine and update number of processors in "Oracle VM VirtualBox Manager".